In a world driven by technology, the race to maximize the benefits of advanced technologies is intensifying every day. In the manufacturing industry, it is all about making/building smart factories using digital technologies, automation, and advanced data-driven processes in industrial operations.
The increasing use of technology to transform the entire manufacturing industry is what we refer to as Smart Manufacturing. Unlike traditional methods, smart manufacturing leverages AI, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), robotics, and advanced analytics to develop more adaptive, efficient, and sustainable production environments.
For the decision-makers, the smart manufacturing revolution is not only about adopting new and advanced tools, but also about rethinking your their operations to improve productivity, lower costs, and enhance resilience. According to a recent study, the global smart manufacturing market is expected to reach $787 billion by 2030, underscoring the need for businesses like yours to align with these innovations.
How Are Industry 4.0 Technologies Redefining Smart Manufacturing?
Industry 4.0 technologies are the actual drivers of smart manufacturing, enabling agility, precision, and scalability:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Artificial Intelligence helps manufacturing units optimize production scheduling, predictive maintenance, and demand forecasting through real-time decision-making.
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): The increasing use of connected machines, sensors, and systems provides real-time visibility, helping to streamline the production line.
- Robotics & Automation: The increasing use of robotics and automation will enable speed, consistency, and safety in production.
- Advanced Analytics & Digital Twins: Simulate processes, monitor KPIs, and prevent downtime.
AI-driven predictive maintenance can help manufacturing units minimize their machine downtime by as much as 30–50% and increase asset lifespan by 20–40%. By leveraging these advanced technologies, manufacturing units can achieve greater operational stability while unlocking new revenue streams.
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.Which Mega-Trends Will Shape Smart Manufacturing in 2025?
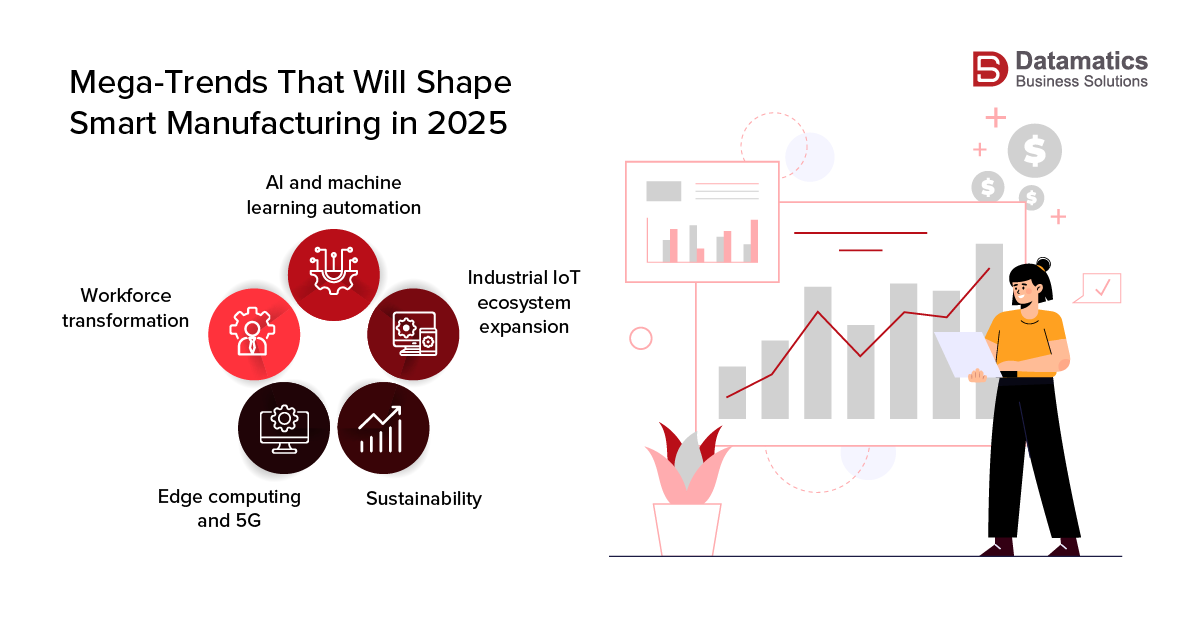
Based on our research and analysis, the following five mega-trends are expected to dominate the evolution of smart manufacturing:
- AI and machine learning automation: Modern manufacturers will increase their use of AI and Machine Learning for real-time decision-making and scalable process improvements, ranging from automatic quality control to supply chain optimization.
- Industrial IoT ecosystem expansion: The explosion of connected devices will promote end-to-end visibility, asset tracking, and predictive maintenance.
- Sustainability: The manufacturing industry is expected to see an increase in the use of energy-efficient systems and data-driven resource management to meet its ESG goals.
- Edge computing and 5G: The rapid advancements in faster networks will enable real-time analysis and lower latency throughout operations.
- Workforce transformation: Manufacturers will grow their focus on upskilling teams and leveraging talent to harness new technologies.
Nearly 92% manufacturers globally believe that smart manufacturing will continue to be the main driver of competitiveness by 2028, with tangible benefits including a 10–20% rise in output and productivity gains up to 20%.
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.How Are Different Industries Adopting Smart Manufacturing?
The adoption of AI/IoT in the global manufacturing is influenced by operational needs and digital maturity, and also varies by industry, below is adoption status by different industries:
- Automotive: manufacturing sector shows higher digital adoption, driven by robotics, AI, and digital twins. Key players like Tesla, BMW, and Toyota are leading innovations. However, higher costs and cybersecurity risks remain major challenges.
- Pharmaceuticals: the adoption of smart factory technology in this sector is moderate to high, with advancements in AI for drug discovery and IoT for logistics. Companies such as Pfizer and Moderna are pushing forward, however regulatory complexities and slower validation processes hinder the rapid progress.
- Oil & Gas: industry has seen Moderate adoption of the technology with AI/ML for predictive maintenance and drone usage. Companies like Shell and Schlumberger lead, but legacy systems and hazardous environments pose barriers.
- Power Generation: AI for grid optimization and IoT in renewables are enhancing smart factory operations in power generation area, however, many challenges rise due to aging infrastructure, limiting faster adoption.
- Power Transmission & Distribution: Moderate adoption of smart grids and blockchain energy trading is underway however, cybersecurity risks being a significant concern. Key suppliers include Schneider Electric and ABB
- Aerospace: Adoption of smart factory is strong especially the use of 3D printing and digital twins is higher in this sector. Boeing and Airbus are at the forefront, but stringent safety regulations and longer certification processes slow the deployments.
- Chemicals: industry has seen moderate adoption driven by AI for process optimization and IoT monitoring. However, the implementation faces challenges due to high capital requirements and hazardous operating conditions.
- Semiconductors: This industry leads in digital adoption with highly automated fabs and AI-driven defect detection. TSMC and Intel dominate, though geopolitical risks affect supply stability.
Across the manufacturing sector, nearly 67% of industrial companies have already implemented some form of smart manufacturing, but adoption levels range from 45% in SMEs to over 80% in large enterprises.
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.What Are the Costs of Adoption in Smart Manufacturing?
While smart manufacturing is certainly the future, for small to medium-sized manufacturers, there is serious cost arbitrage involved. Hence, when you are evaluating smart manufacturing, here are a few cost considerations that you need to pay attention to
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.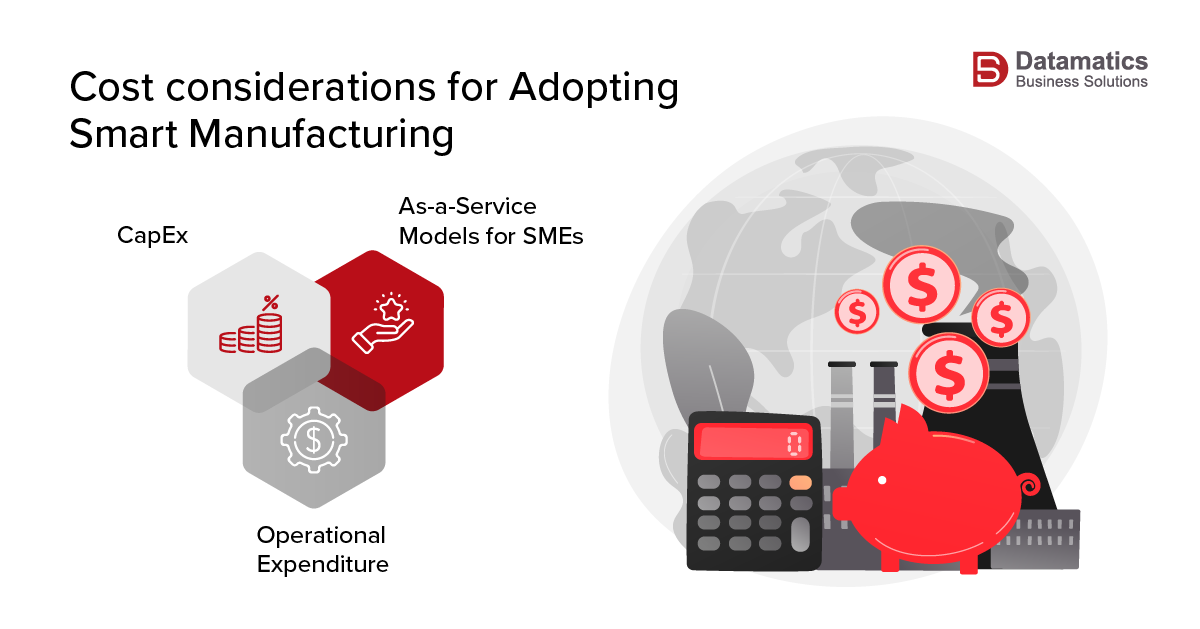
- CapEx encompasses the initial investments required to implement smart manufacturing solutions. Key components include:
Hardware: These costs include purchase of sensors, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), robotics, and edge devices.
Software: Acquiring licenses for manufacturing execution systems (MES), enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and AI/ML platforms.
Infrastructure: Upgrading networks, data centers, and integrating cloud platforms.
These expenses are capitalized and depreciated over time, impacting the balance sheet.
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.- Operational Expenditure (OpEx): OpEx refers to the ongoing costs of operating and maintaining smart manufacturing systems. This includes
Maintenance: Regular upkeep of hardware and software systems.
Cloud Services: Subscriptions for cloud storage, computing, and software-as-a-service (SaaS) platforms.
Cybersecurity: Implementing and updating security measures to protect digital assets.
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.- As-a-Service Models for SMEs
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often leverage as-a-service models to mitigate high upfront costs
Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS): Allows businesses to utilize robotics solutions on a subscription basis, converting CapEx to OpEx.
AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS): Provides access to AI tools and platforms without significant initial investments
A good example here is the 20% YoY rise of robotics-as-a-service adoption, enabling small-sized manufacturers to gain access to automation without heavy upfront investments. It is estimated that ~75% of manufacturing execution systems will be delivered as SaaS solutions, shifting the financial model from Capex to Opex.
Who Are the Key Players in the Smart Manufacturing Ecosystem?
The smart factory market is diverse with large, established companies and start-ups. Few of the key players include technology giants like ABB, Bosch, Siemens, Schneider Electric, Rockwell Automation, Mitsubishi Electric, GE and Emerson Electric etc.
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.ABB
Smart Factory Offerings:
- ABB Ability Platform: IIoT and AI platform for analytics, predictive maintenance, and digital twins
- System 800xA: Distributed control system for process automation
- GoFa Cobots: Collaborative robots for electronics and healthcare
- EMI Software: Collaborative production management with MES functionality
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.Industry Strengths:
- Energy: Leads in power grids and renewable energy integration
- Electronics: GoFa cobots enhance precision manufacturing.
- Healthcare: Supplies automation for medical device production
Geographic Strengths:
- Europe: Strong in Switzerland and Germany
- Asia-Pacific: Expanding in India and Japan
- North America: Growing in energy and electronics
- Specific Strength: ABB’s Ability platform and robotics excel in energy and electronics, with a balanced global presence
Bosch
Smart Factory Offerings:
- Nexeed Industrial Application System: An IIoT platform for real-time data collection, analytics, and predictive maintenance, integrating AI for quality control and energy optimization.
- AIoT Solutions: AI and IoT for self-optimizing production, notably in its Dresden wafer fab, using digital twins and smart sensors.
- Bosch Connected Industry: modular software for automation, including condition monitoring and production tracking.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): APAS robots for flexible manufacturing in automotive and electronics.
Industry Strengths:
- Automotive: Offers sensors, semiconductors, and driver assistance systems, enhancing production efficiency (e.g., 30% productivity gains in wafer production).
- Semiconductors: Dresden fab leverages AIoT for defect detection and process optimization
- Consumer Goods: Supplies automation solutions for high-speed production lines.
Geographic Strengths:
- Bosch has strong presence in Germany, with advanced smart factories in Stuttgart and Dresden.
- The company is expanding in China and India, focusing on automotive and electronics
- Bosch continues to grow its presence in the automotive manufacturing hubs especially in North America
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.Siemens
Smart Factory Offerings:
- MindSphere Platform: Cloud-based IIoT system for data analytics and digital twins
- SIMATIC Automation Systems: PLCs and control systems for industrial automation
- TIA Portal: Comprehensive framework for automation, offering low/no-code solutions
- Industrial Copilot (2025): AI agents for automation tasks in manufacturing [^50]
- Specific Strength: Siemens leads in industrial software and digital automation, with a strong European base and versatile TIA Portal.
Industry Strengths:
- Automotive: Supports BMW and Volkswagen with digital twins and robotics.
- Machinery: automation projects, leveraging SIMATIC.
- Healthcare: Siemens Healthineers uses IIoT for medical device production.
Geographic Strengths:
- Siemens is dominant in Germany and UK, with strong TIA Portal adoption
- It is expanding APAC especially in China and India
- Also growing in automotive and machinery market in North America
Schneider Electric
Smart Factory Offerings:
- EcoStruxure Platform: An IIoT and AI-driven platform for energy management, automation, and sustainability, featuring EcoStruxure Plant for manufacturing.
- Augmented Reality and Digital Twins: Optimizes production processes and reduces downtime.
- Azure AI Foundry Copilot: Collaboration with Microsoft for generative AI to automate repetitive tasks (2025)
- Cybersecurity Solutions: Protects IoT devices and cloud-based systems
Industry Strengths:
- Food and Beverage: Enhances quality control and energy efficiency (e.g., Nestlé plants)
- Data Centers: Supports high-demand automation for infrastructure
- Utilities: Provides smart grid and energy management solutions
- Specific Strength: Schneider’s EcoStruxure excels in sustainability and energy management, with robust growth in Asia-Pacific and data center automation.
Geographic Strengths:
- North America: Strong in data centers and industrial automation.
- Asia-Pacific: High growth in China and India (double-digit revenue growth in Q1 2024)
- Middle East & Africa: Expanding in smart city projects.
Rockwell Automation
Smart Factory Offerings:
- FactoryTalk Platform: Includes FactoryTalk Optix and InnovationSuite for IIoT, analytics, and predictive maintenance
- Allen-Bradley PLCs: High-performance controllers for discrete manufacturing
- Plex Systems (MES): Cloud-based manufacturing execution system for real-time production tracking
- Cybersecurity and Edge Computing: Enhances secure data integration
Industry Strengths:
- Automotive: Rockwell dominates discrete manufacturing
- Consumer Goods: Optimizes high-speed production lines
- Pharmaceuticals: FactoryTalk supports compliance and quality control
Geographic Strengths:
- Rockwell is a strong player with deep automotive industry penetration in North America
- Asia-Pacific: Expanding through Cisco partnerships
- Rockwell continue to grow in discrete manufacturing sectors in Europe
- Specific Strength: Rockwell’s FactoryTalk and PLCs lead in North America discrete manufacturing, with strong partnerships enhancing IIoT capabilities
You can also read: Next-Gen EV Battery Technologies: Your Gateway to the Electric Revolution
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel. Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.Regional and Local Players
While global giants like Bosch, Siemens, and Schneider Electric dominate AI/IoT smart manufacturing, regional and locally large companies play a critical role in advancing Industry 4.0 adoption. These firms, often mid-sized or large within their regions, leverage AI and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technologies to enhance operational efficiency, meet local market demands, and compete globally.
North America
- Key Players: PTC (USA), Epicor Software Corporation (USA), Infor (USA).North American firms leverage advanced infrastructure and 5G networks for IIoT adoption. PTC’s ThingWorx platform is widely used for predictive maintenance in automotive and aerospace. Epicor focuses on ERP-integrated IoT for discrete manufacturing, while Infor’s CloudSuite Industrial targets real-time analytics
Europe
- Key Players: Festo (Germany), Kuka (Germany), Beckhoff Automation (Germany) European firms align with Industry 4.0 initiatives, supported by EU funding. Festo integrates AI-driven pneumatics for automation, Kuka deploys cobots for flexible production, and Beckhoff’s TwinCAT supports real-time control in smart factories.
Asia-Pacific
- Key Players: Advantech (Taiwan), Omron (Japan), Fanuc (Japan).
Trends: Asia-Pacific leads in growth driven by smart city initiatives and government policies like China’s “Made in China 2025.” Advantech’s WISE-PaaS platform supports – (e.g., WISE-PaaS, WISE-4000) supports industrial automation, Omron focuses on AI-driven quality control, and Fanuc integrates robotics with IoT for automation
Other Regions (Middle East, Africa, South America)
- Key Players: AspenTech (South Africa), Tecnicas Reunidas (Spain, active in Middle East), WEG (Brazil).
Emerging markets focus on cost-effective IIoT solutions. AspenTech’s asset optimization software is used in oil and gas, Tecnicas Reunidas deploys IIoT for energy.
Each player in the smart manufacturing space has played a role in reshaping the landscape. While some offer holistic ecosystems, others provide niche technologies.
What Regional Insights Should You Consider for Smart Manufacturing?
The evolution of smart manufacturing is shaping up differently across the globe. Here are some regional insights that you must consider for smart manufacturing:
- North America: Strong adoption in aerospace, automotive, and defense, backed by government incentives.
- Europe: The priority is sustainability, energy efficiency, and carbon neutrality in the adoption of Industry 4.0.
- Asia-Pacific: One of the fastest-growing markets, with China leading in IIoT adoption and India emerging as a smart manufacturing hub.
- Middle East & Africa: Smart manufacturing is tied to industrial diversification strategies, especially in Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030.
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.According to industry insights, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to account for over 40% of the smart manufacturing market by 2030, making it the most dynamic growth area.
Why Should You Invest in Custom Research Before Adopting Smart Manufacturing?
By investing in custom research, you lower your risks, accelerate ROI, and gain a significant competitive edge in a fast-evolving ecosystem.The promise of smart manufacturing is transformative, factories of the future can achieve up to 30% gains in operational efficiency and 20–40% reductions in maintenance costs through predictive analytics. Yet, this potential is tempered by real-world complexities.
The demand side (enterprises adopting these solutions) faces challenges like high upfront investments, evolving skill requirements, and the risk of technology lock-in. On the supply side (solution providers, OEMs, and technology vendors), fragmentation, inconsistent standards, and uneven regional maturity complicate the decision-making process.
Without the right intelligence, manufacturers risk over-investing in technologies misaligned with their scale or region—or underestimating the organizational and cultural change required for adoption. This is where custom market research becomes indispensable.
A seasoned custom research provider helps manufacturers make fact-based, context-specific decisions by addressing both sides of the ecosystem:
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.Benchmark adoption patterns in your industry (Demand-side intelligence)
Understand how your peers and competitors are integrating smart technologies. For instance, while 67% of global manufacturers are piloting AI-driven solutions, only 21% have scaled them enterprise-wide. Custom research shows you where you truly stand relative to your market.
Identify the most cost-effective technologies for your scale (Supply-side fit)
With hundreds of smart sensors, MES platforms, and IIoT solutions in the market, not every option suits mid-sized firms versus global enterprises. Research helps you shortlist technologies that deliver the highest ROI relative to your production scale, operational complexity, and budget constraints.
Evaluate vendor capabilities and long-term ROI (Supply chain resilience):
Understand regional regulations and sustainability mandates (Policy and compliance lens):
Governments worldwide are linking subsidies and tax incentives to Industry 4.0 adoption but with strict compliance to data sovereignty, energy efficiency, and ESG standards. Custom research helps you navigate regional nuances—such as Europe’s Digital Product Passport mandate or the U.S. CHIPS Act incentives—so you avoid regulatory pitfalls while leveraging available benefits.
Understand regional regulations and sustainability mandates (Policy and compliance lens):
Nearly 70% of manufacturers cite workforce upskilling as a top barrier to digital transformation. Custom research can uncover talent availability in your region, identify reskilling best practices, and highlight automation-human collaboration models to ease adoption challenges.
The Payoff of Research-Led Adoption
By investing in custom research before diving into smart manufacturing, manufacturers can:
- Lower risks by avoiding mismatched technologies and unprepared vendors.
- Accelerate ROI by focusing only on scalable, high-impact use cases.
- Stay competitive by aligning with industry adoption curves and regulatory requirements.
- Future-proof operations by accounting for talent, sustainability, and supply chain resilience.
In an ecosystem that is both opportunity-rich and risk-laden, custom research acts as your radar—scanning not just the road ahead, but also the blind spots. It ensures your smart manufacturing journey is built on foresight, not trial and error.
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.Conclusion: How Can Smart Manufacturing Power Your Growth Strategy?
For modern manufacturers, smart manufacturing is not just an efficiency play it is a strategic lever for long-term growth and resilience. By harnessing the combined power of AI, IIoT, robotics, digital twins, and advanced analytics, organizations can achieve:
- Demand-Side Benefits (Enterprise Gains):
- Unlock up to 30% improvements in overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and 20–40% reductions in maintenance costs through predictive and prescriptive analytics.
- Enable mass customization to meet evolving customer expectations while lowering lead times.
- Generate new revenue streams via data-driven services and value-added digital offerings.
- Supply-Side Benefits (Vendor & Ecosystem Strength):
- Build resilience into global supply chains by using real-time visibility platforms and digital twins to model disruptions.
- Reduce dependence on fragmented vendor ecosystems by leveraging data-backed insights to select scalable, interoperable platforms.
- Strengthen cybersecurity posture by proactively evaluating vendor safeguards critical as 74% of manufacturers experienced a cyber-incident in the last 12 months.
- Ecosystem Perspective (Regulatory & Market Alignment):
- Stay ahead of evolving sustainability mandates, such as the EU’s Digital Product Passport or U.S. CHIPS Act incentives.
- Align with global ESG imperatives, which now influence over 70% of investor decisions (EY).
- Secure competitive positioning in global trade by aligning with Industry 4.0 roadmaps that are increasingly linked to government subsidies and tax credits.
Yet, with opportunity comes risk. Many manufacturers stumble when making uninformed technology bets, misaligning investments, or underestimating workforce transformation needs. This is why custom research and business intelligence are not optional they are mission-critical.
The right research partner will help you:
- Assess market readiness and peer adoption curves.
- Prioritize technologies that fit your scale and strategic vision.
- Evaluate vendors for long-term viability and ROI.
- Navigate regulatory, sustainability, and workforce challenges.
Smart manufacturing can power not just operational efficiency, but also strategic differentiation, resilience, and growth in a volatile global landscape. The key lies in making decisions grounded in intelligence and not assumptions.
Ready to unlock the full potential of smart manufacturing? Contact us at marketing@datamaticsbpm.com, and let’s chart a research-driven path to your Industry 4.0 journey.
 Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.
Select an element to maximize. Press ESC to cancel.